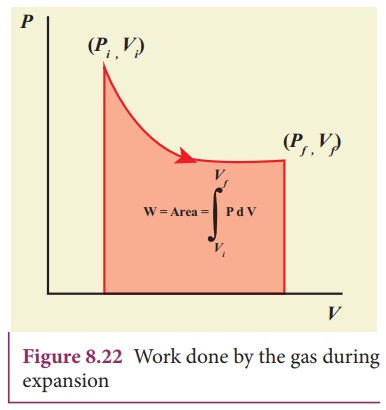
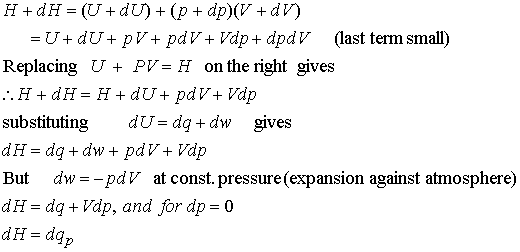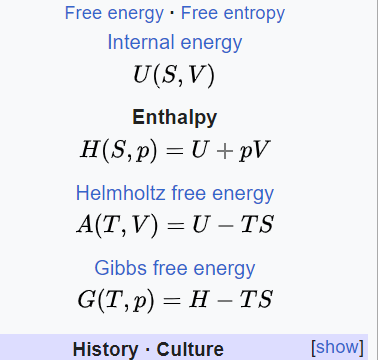15.The relation between U,P and V for an ideal gas is U=2+3PV . The gas is a)monoatomic b)diatomic c)polyatomic d)either monoatomic or diatomic

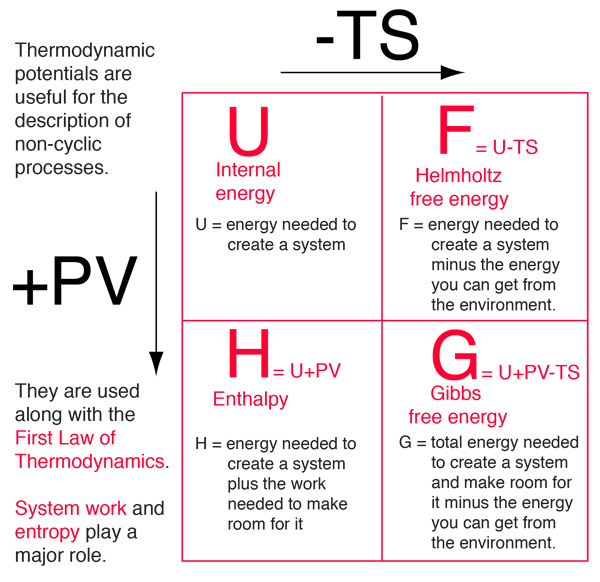
Difference Between Enthalpy and Internal Energy | Definition, Units, Formula for Calculation, Properties, Examples

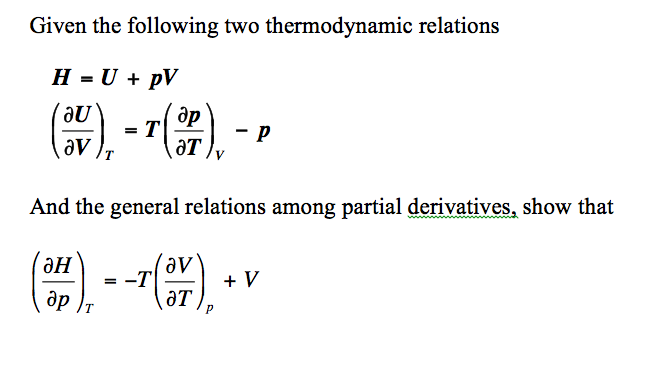
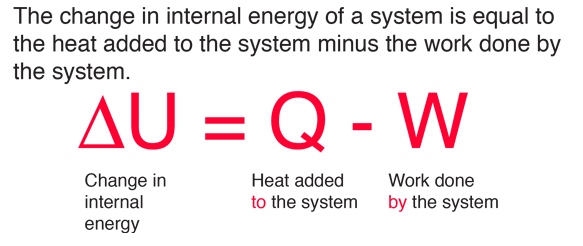
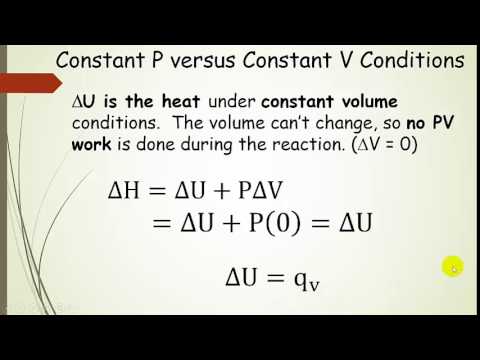
With the help of first law of thermodynamics and H = U + pv, prove dH = qp - Chemistry - Thermodynamics - 3326649 | Meritnation.com
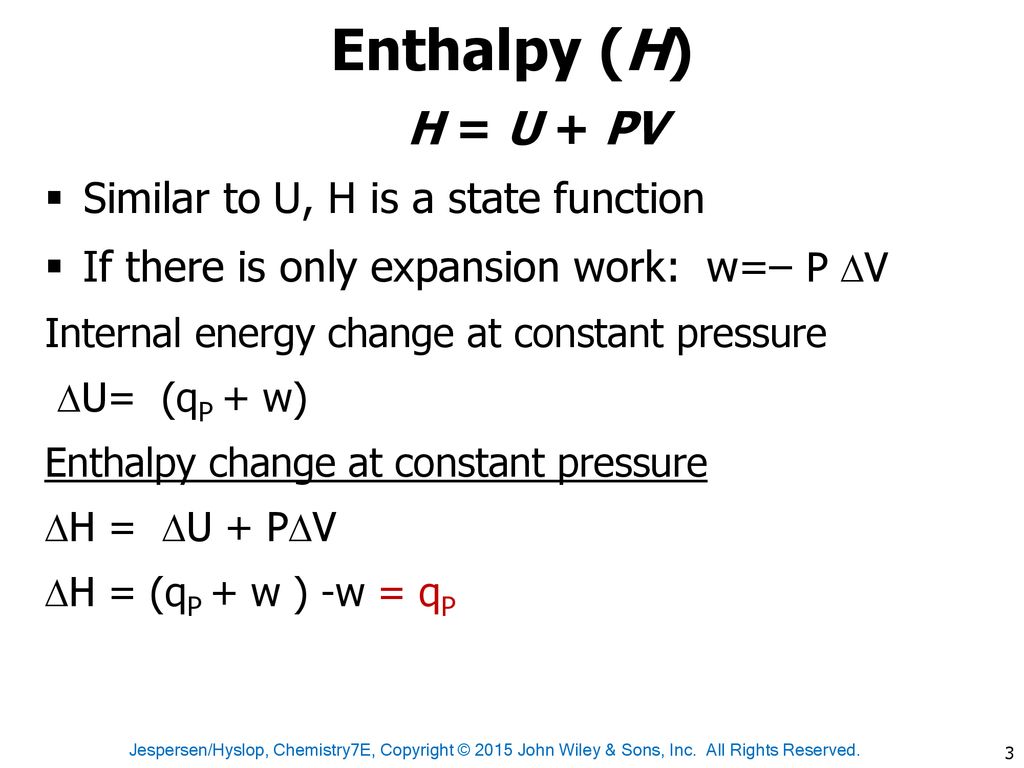
Derive the relation between ∆H and ∆U for an ideal gas. Explain each term involved in the equation. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community