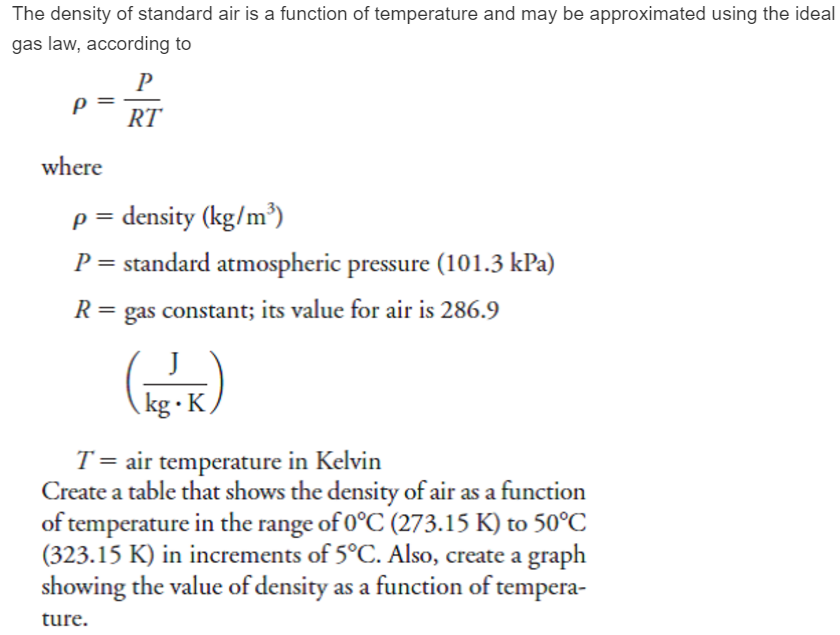
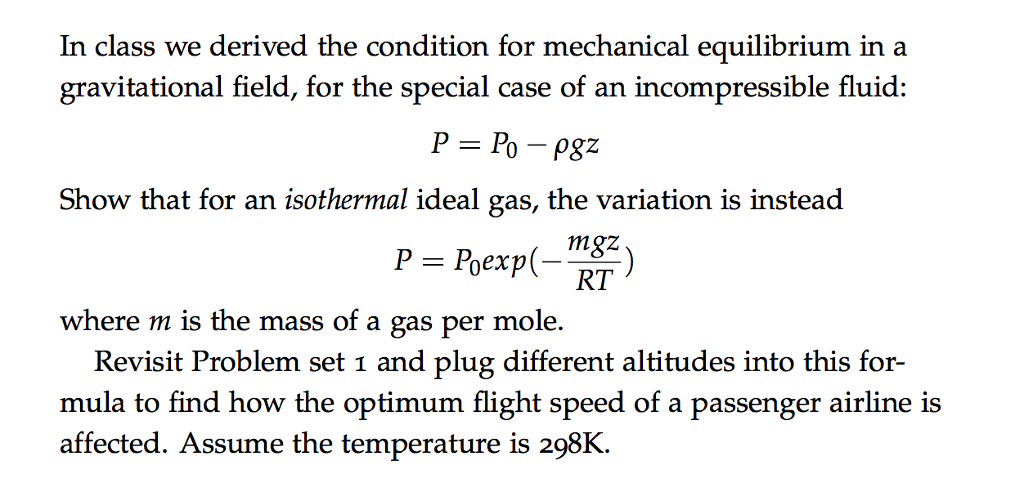
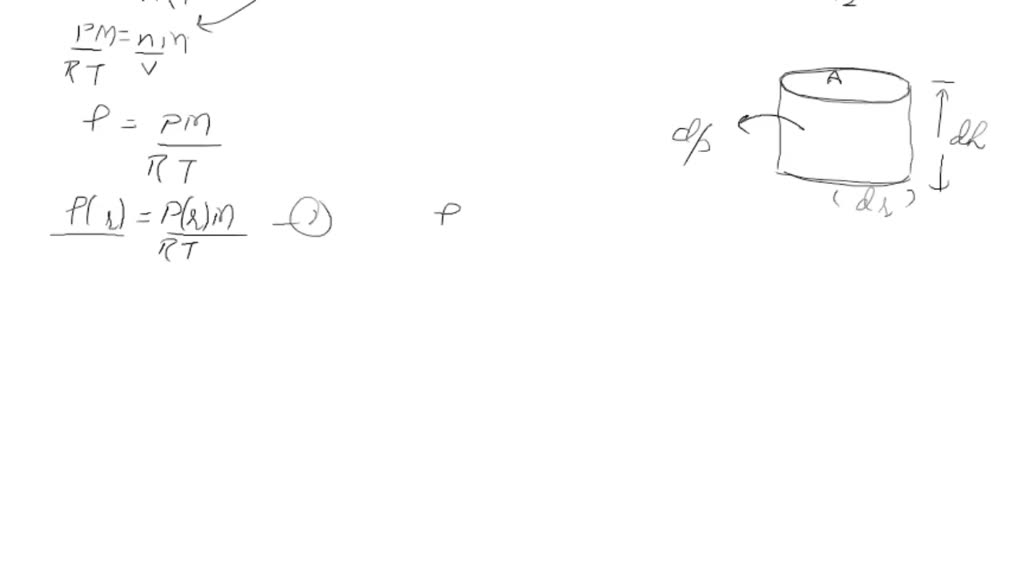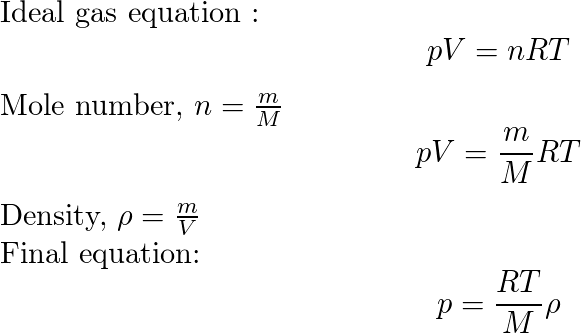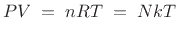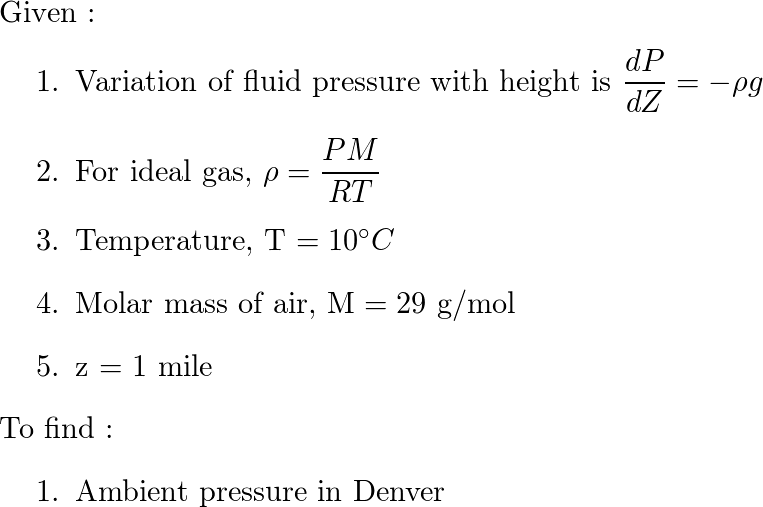Lecture 2: Energy in the Atmosphere Vertical structure of the static atmosphere Basics from physics: force, work, heat Transferring energy in the atmosphere. - ppt download

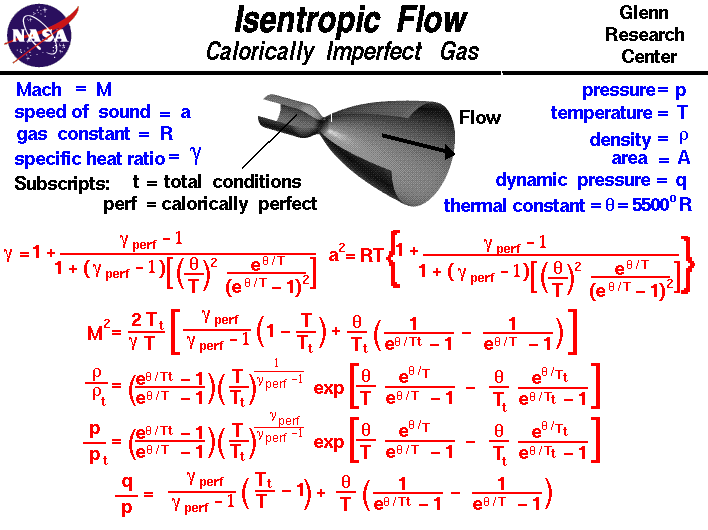
Use the formula v = √(gammaP/ρ) to explain why the speed of sound in air(a) is independent of pressure,(b) increases with temperature, (c) Increases with humidity .
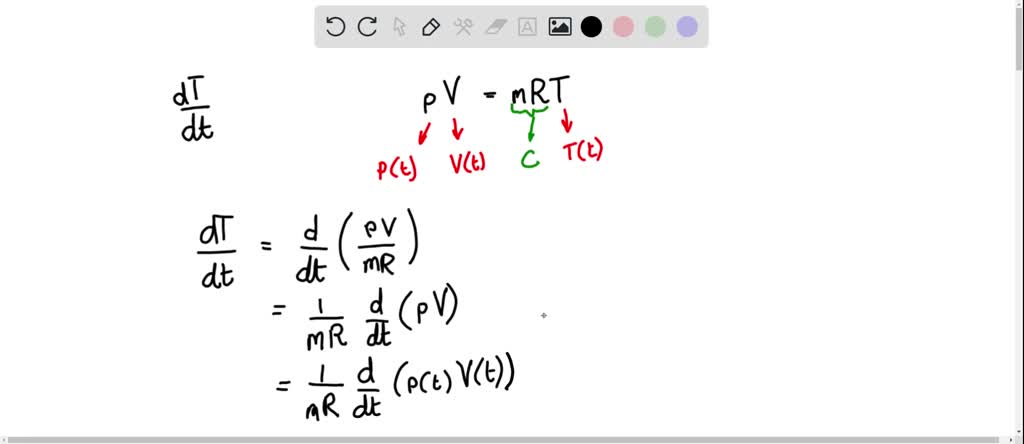
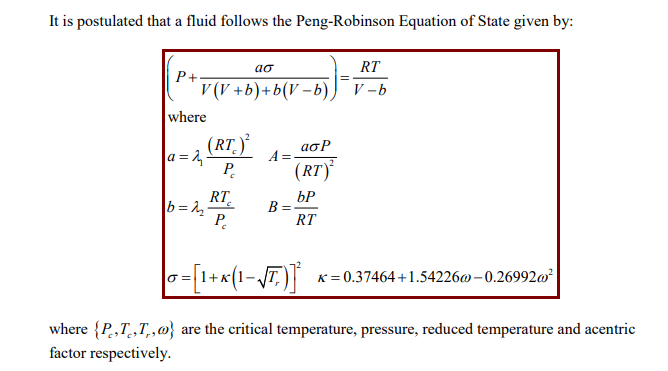
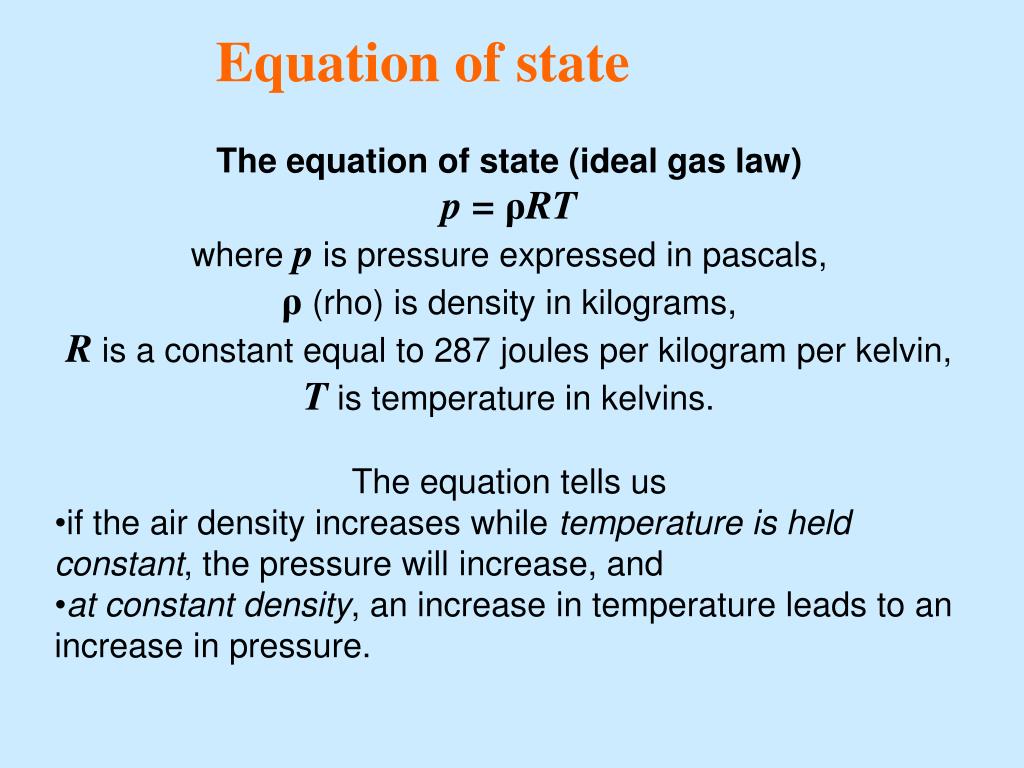
SOLVED: Develop the time averaged form of the equation of state for a perfect gas, P=(rho)RT, accounting for turbulent fluctuations in the instantaneous pressure, p, density, (rho) and temperature, T.